
The neutral tie block is grounded at the center tap of the transformer which supplies the house, and the ground tie block is tied directly to ground via a ground stake or other grounding mechanism. One recent variation which is in force in some locations is the requirement that the neutral tie block and ground wire tie block be separate.
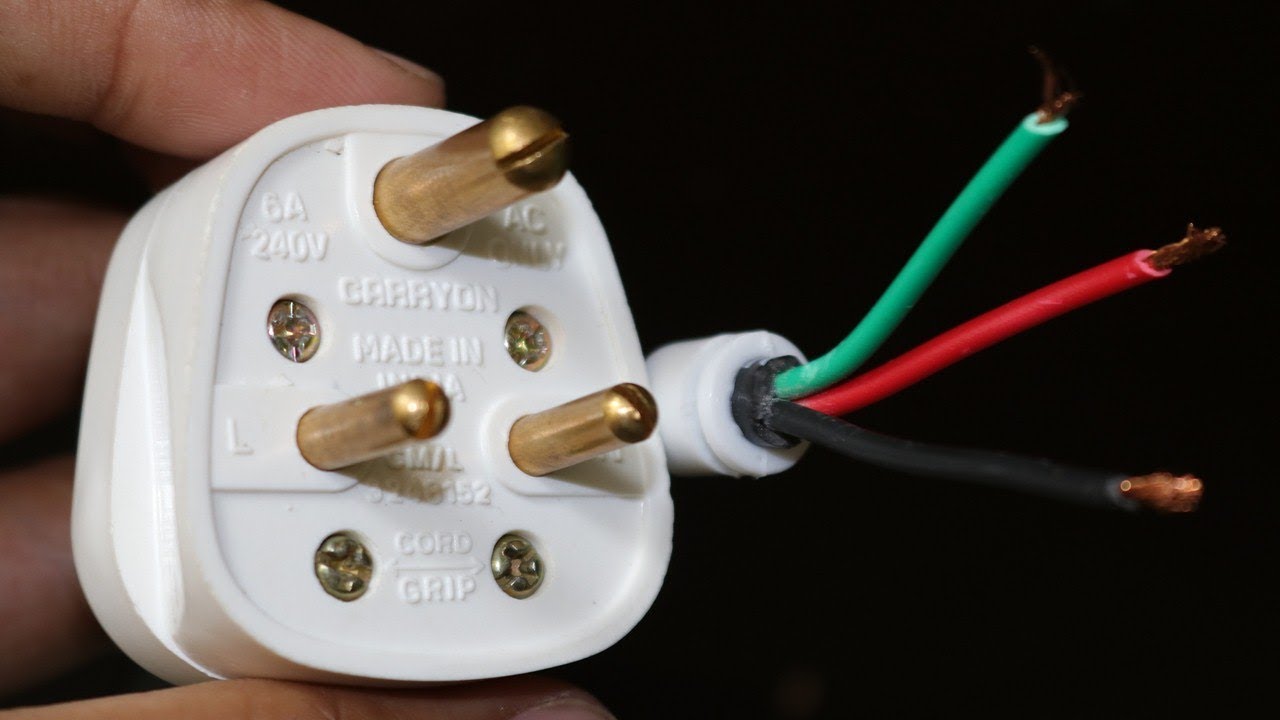
POWER PLUG WIRING CODE
No attempt to summarize the code will be made here, but a few examples may be instructive. For example, current code dictates three-prong polarized receptacles and dictates the use of ground fault interrupters in locations where an electrical appliance may be dropped in water. electrical wiring is governed by a general electrical code. A non-polarized plug may have the switch in the neutral leg and thus be a shock hazard even when it is switched off. The narrower prong is the "hot" lead and the switch to the appliance is placed in that lead, gauranteeing that no voltage will reach the appliance when it is switched off. The wider prong on the polarized plug will permit it to be plugged in only with the correct polarity. Parallel wiring is the standard for 120 volt circuits in the entire house, making possible the independent use of all appliances, supplied by the same voltage. They are wired in parallel so that two appliances which are plugged into the receptacle receive the same voltage, but can draw different amounts of electric current. Prongs are inserted into the holes of an outlet or receptacle to establish the electrical connection between the appliance and the main power supply. The two receptacles in a common "duplex" receptacle receive power from the same circuit leading from the main electrical supply panel. The ground wire is not a part of the electrical circuit, but is desirable for prevention of electric shock. The neutral wire carries the current back to the electrical panel and from there to the earth (ground). If an appliance is plugged into the receptacle, then electric current will flow through the appliance and then back to the wider prong, the neutral. The high voltage (about 120 volts effective, 60 Hz AC) is supplied to the smaller prong of the standard polarized U.S. HyperPhysics***** Electricity and magnetism What happens to the electric charge in household circuits? , both hot wires can be used to produce a 240 volt circuit. For higher power applications like clothes dryers, electric ranges, air conditioners, etc. This versatile design allows the use of either hot wire to supply the standard 120 volt household circuits. The two 120 volt wires are obtained by grounding the centertap of the transformer supplying the house so that when one hot wire is swinging positive with respect to ground, the other is swinging negative. The procedure for 110-volt plug wiring is made easier by the fact that youre dealing with 14- or 12-gauge wires, instead of the beefier wires needed for 220-volt circuits.
household wiring design has two 120 volt "hot" wires and a neutral which is at ground potential. Household Electric Circuits Household Wiring


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
